本文系統(tǒng):centos6.5_x64
三臺主機(jī):nginx主機(jī),hostname: master.lansgg.com? ip: 192.168.10.128??
????????? apache主機(jī),hostname: client1.lansgg.com ip:? 192.168.10.129
一、nginx 地址重定向
二、nginx 反向代理
1、地址重定向:是指當(dāng)使用者瀏覽某個網(wǎng)址時,將他導(dǎo)向到另一個網(wǎng)址的技術(shù)。常用在把一串很長的網(wǎng)址,轉(zhuǎn)成較短的網(wǎng)址。因為當(dāng)要傳播某網(wǎng)站時,常常因為網(wǎng)址太長,不好記憶;又有可能因為換了網(wǎng)路的免費(fèi)網(wǎng)頁空間,網(wǎng)址又必須要變更,不知情的使用者還以為網(wǎng)站關(guān)閉了。這時就可以用網(wǎng)路上的轉(zhuǎn)址了。這個技術(shù)使一個網(wǎng)頁是可借由不同的統(tǒng)一資源定位符(url)連結(jié)。
1.1、這 個模塊允許使用正則表達(dá)式重寫uri(需pcre庫),并且可以根據(jù)相關(guān)變量重定向和選擇不同的配置。如果這個指令在server字段中指定,那么將在被 請求的location確定之前執(zhí)行,如果在指令執(zhí)行后所選擇的location中有其他的重寫規(guī)則,那么它們也被執(zhí)行。如果在location中執(zhí)行這 個指令產(chǎn)生了新的uri,那么location又一次確定了新的uri。這樣的循環(huán)可以最多執(zhí)行10次,超過以后nginx將返回500錯誤
正則表達(dá)式匹配,其中:
* ~ 為區(qū)分大小寫匹配
* ~* 為不區(qū)分大小寫匹配
* !~和!~*分別為區(qū)分大小寫不匹配及不區(qū)分大小寫不匹配
文件及目錄匹配,其中:
* -f和!-f用來判斷是否存在文件
* -d和!-d用來判斷是否存在目錄
* -e和!-e用來判斷是否存在文件或目錄
* -x和!-x用來判斷文件是否可執(zhí)行
flag標(biāo)記有:
* last 相當(dāng)于apache里的[l]標(biāo)記,表示完成rewrite
* break 終止匹配, 不再匹配后面的規(guī)則
* redirect 返回302臨時重定向 地址欄會顯示跳轉(zhuǎn)后的地址
* permanent 返回301永久重定向 地址欄會顯示跳轉(zhuǎn)后的地址
一些可用的全局變量有,可以用做條件判斷
$args,?請求中的參數(shù); $content_length,?http請求信息里的"content-length"; $content_type,?請求信息里的"content-type"; $document_root,?針對當(dāng)前請求的根路徑設(shè)置值; $document_uri,?與$uri相同; $host,?請求信息中的"host",如果請求中沒有host行,則等于設(shè)置的服務(wù)器名; $limit_rate,?對連接速率的限制; $request_method,?請求的方法,比如"get"、"post"等; $remote_addr,?客戶端地址; $remote_port,?客戶端端口號; $remote_user,?客戶端用戶名,認(rèn)證用; $request_filename,?當(dāng)前請求的文件路徑名 $request_body_file $request_uri,?請求的uri,帶查詢字符串; $query_string,?與$args相同; $scheme,?所用的協(xié)議,比如http或者是https,比如rewrite?^(.+)$?$scheme://example.com$1?redirect; $server_protocol,?請求的協(xié)議版本,"http/1.0"或"http/1.1"; $server_addr,?服務(wù)器地址,如果沒有用listen指明服務(wù)器地址,使用這個變量將發(fā)起一次系統(tǒng)調(diào)用以取得地址(造成資源浪費(fèi)); $server_name,?請求到達(dá)的服務(wù)器名; $server_port,?請求到達(dá)的服務(wù)器端口號; $uri,?請求的uri,可能和最初的值有不同,比如經(jīng)過重定向之類的。
rewrite 指令:可以使用在 server, location, if 區(qū)域;
語法:rewrite regex replacement flag
按照相關(guān)的正則表達(dá)式與字符串修改uri,指令按照在配置文件中出現(xiàn)的順序執(zhí)行。?
可以在重寫指令后面添加標(biāo)記。?
如果替換的字符串以http://開頭,請求將被重定向,并且不再執(zhí)行多余的rewrite指令。?
尾部的標(biāo)記(flag)可以是以下的值:
-
last – 完成重寫指令,之后搜索相應(yīng)的uri或location。
-
break – 完成重寫指令。
-
redirect – 返回302臨時重定向,如果替換字段用http://開頭則被使用。
-
permanent – 返回301永久重定向。
注 意如果一個重定向是相對的(沒有主機(jī)名部分),nginx將在重定向的過程中使用匹配server_name指令的“host”頭或者 server_name指令指定的第一個名稱,如果頭不匹配或不存在,如果沒有設(shè)置server_name,將使用本地主機(jī)名,如果你總是想讓nginx 使用“host”頭,可以在server_name使用“*”通配符(查看http核心模塊中的server_name)。例如:
rewrite?^(/download/.*)/media/(.*)..*$?$1/mp3/$2.mp3?last; rewrite?^(/download/.*)/audio/(.*)..*$?$1/mp3/$2.ra?last; return?403;
但是如果我們將其放入一個名為/download/的location中,則需要將last標(biāo)記改為break,否則nginx將執(zhí)行10次循環(huán)并返回500錯誤。
location?/download/?{ ?rewrite?^(/download/.*)/media/(.*)..*$?$1/mp3/$2.mp3?break; ?rewrite?^(/download/.*)/audio/(.*)..*$?$1/mp3/$2.ra?break; ?return?403; }
如果替換字段中包含參數(shù),那么其余的請求參數(shù)將附加到后面,為了防止附加,可以在最后一個字符后面跟一個問號:
rewrite?^/users/(.*)$?/show?user=$1??last;
注意:大括號({和}),可以同時用在正則表達(dá)式和配置塊中,為了防止沖突,正則表達(dá)式使用大括號需要用雙引號(或者單引號)。例如要重寫以下的url:
/photos/123456
為:
/path/to/photos/12/1234/123456.png
則使用以下正則表達(dá)式(注意引號):
rewrite?"/photos/([0-9]?{2})([0-9]?{2})([0-9]?{2})"?/path/to/photos/$1/$1$2/$1$2$3.png;
如果指定一個“?”在重寫的結(jié)尾,nginx將丟棄請求中的參數(shù),即變量$args,當(dāng)使用$request_uri或$uri&$args時可以在rewrite結(jié)尾使用“?”以避免nginx處理兩次參數(shù)串。?
在rewrite中使用$request_uri將www.example.com重寫到example.com:
server?{ ?server_name?www.example.com; ?rewrite?^?http://example.com$request_uri??permanent; }
同樣,重寫只對路徑進(jìn)行操作,而不是參數(shù),如果要重寫一個帶參數(shù)的url,可以使用以下代替:
if?($args?^~?post=100){ ?rewrite?^?http://example.com/new-address.html??permanent; }
注意$args變量不會被編譯,與location過程中的uri不同(參考http核心模塊中的location)
示例:當(dāng)訪問www.lansgg.com的時候跳轉(zhuǎn)到www.aries.com;
?server?{ ??listen?80?default_server; ??server_name??www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ??access_log??logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ??error_log??logs/lansgg.error.log; ??root???/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ??index?index.html; ??rewrite?^/?http://www.aries.com/; ??}
break 指令 可使用server, location, if 區(qū)域; 中止rewirte,不在繼續(xù)匹配
last 指令 可server, location, if? 區(qū)域;
last與break的區(qū)別在于,last并不會停止對下面location的匹配。
測驗一下break與last的區(qū)別
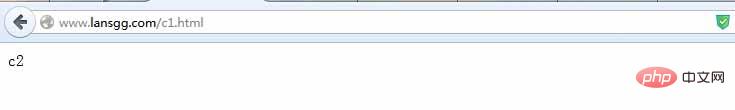
?server?{ ?listen?80?default_server; ?server_name?www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ?access_log?logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ?error_log?logs/lansgg.error.log; ?root??/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ?index?index.html; ?location?/c1.html?{ ?rewrite?/c1.html?/c2.html?break; ?} ?location?/c2.html?{ ?return?508; ?} ?} [root@master?sbin]#?echo?"c1"?>?/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg/c1.html [root@master?sbin]#?echo?"c2"?>?/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg/c2.html
使用break會停止匹配下面的location,直接發(fā)起請求,他會顯示c2的內(nèi)容;
 ??
??
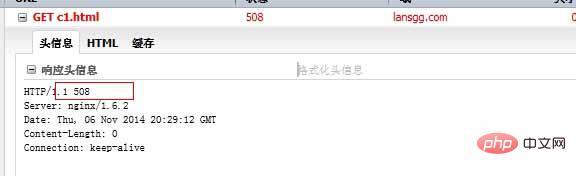
使用last的話,會繼續(xù)搜索下面是否有符合條件(符合重寫后的/c2.html請求)的location。此時,/c2.html剛好與面location的條件對應(yīng)上了,進(jìn)入花括號{}里面的代碼執(zhí)行,這里會返回508。
?server?{ ?listen?80?default_server; ?server_name?www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ?access_log?logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ?error_log?logs/lansgg.error.log; ?root??/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ?index?index.html; ?location?/c1.html?{ ?rewrite?/c1.html?/c2.html?last; ?} ?location?/c2.html?{ ?return?508; ?} ?}
使用firebug 可以看到;
if 指令 可使用server, location 區(qū)域;
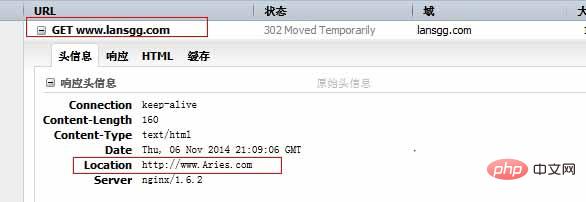
示例:當(dāng)訪問網(wǎng)址的時候跳轉(zhuǎn)到www.aries.com;
?server?{ ??listen?80?default_server; ??server_name??www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ??access_log??logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ??error_log??logs/lansgg.error.log; ??root???/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ??index?index.html; ??if?($http_host?=?www.lansgg.com){ ??rewrite?(.*)?http://www.aries.com; ??} ??}
return 指令 可使用server, location, if? 區(qū)域
語法:return code?
這個指令結(jié)束執(zhí)行配置語句并為客戶端返回狀態(tài)代碼,可以使用下列的值:204,400,402-406,408,410, 411, 413, 416與500-504。此外,非標(biāo)準(zhǔn)代碼444將關(guān)閉連接并且不發(fā)送任何的頭部。
rewrite_log? 指令? 可使用server, location, if? 區(qū)域
啟用時將在error log中記錄notice 標(biāo)記的重寫日志。
set 指令 可使用server, location, if? 區(qū)域
語法:set variable value?
指令設(shè)置一個變量并為其賦值,其值可以是文本,變量和它們的組合。?
你可以使用set定義一個新的變量,但是不能使用set設(shè)置$http_xxx頭部變量的值。
uninitialized_variable_warn 指令 可使用 http, server, location, if? 區(qū)域
語法:uninitialized_variable_warn on|off?
默認(rèn)值:uninitialized_variable_warn on?
開啟或關(guān)閉在未初始化變量中記錄警告日志。?
事實上,rewrite指令在配置文件加載時已經(jīng)編譯到內(nèi)部代碼中,在解釋器產(chǎn)生請求時使用。?
expires 指令 可 http, server, location 區(qū)域
語法: expires [time|epoch|max|off]
默認(rèn)值: expires off
該指令可以控制http應(yīng)答中的“expires”和“cache-control”的頭標(biāo),(起到控制頁面緩存的作用)。可以在time值中使用正數(shù)或負(fù)數(shù)。“expires”頭標(biāo)的值將通過當(dāng)前系統(tǒng)時間加上設(shè)定的 time 值來獲得。
epoch 指定“expires”的值為 1 january, 1970, 00:00:01 gmt。
max 指定“expires”的值為 31 december 2037 23:59:59 gmt,“cache-control”的值為10年。
-1 指定“expires”的值為 服務(wù)器當(dāng)前時間 -1s,即永遠(yuǎn)過期
“cache-control”頭標(biāo)的值由指定的時間來決定:
??? 負(fù)數(shù):cache-control: no-cache
??? 正數(shù)或零:cache-control: max-age = #, # 為指定時間的秒數(shù)s。其他的單位有d(天),h(小時)
“off” 表示不修改“expires”和“cache-control”的值
控制圖片等過期時間為30天,這個時間可以設(shè)置的更長。具體視情況而定
location?~?.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|ico)$?{ ???log_not_found?off;?#不記錄404?not?found?錯誤日志???expires?30d; ???break;??}
控制匹配/resource/或者/mediatormodule/里所有的文件緩存設(shè)置到最長時間
??location?~?/(resource|mediatormodule)/?{ ????root?/opt/demo; ????expires?max; ??}
設(shè)定某個文件的過期時間;這里為600秒,并不記錄訪問日志
location?^~?/html/scripts/loadhead_1.js?{ access_log?off; root?/opt/lampp/htdocs/web; expires?600; break; }
設(shè)置gzip
一般情況下壓縮后的html、css、js、php、jhtml等文件,大小能降至原來的25%,也就是說,原本一個100k的html,壓縮后只剩下25k。這無疑能節(jié)省很多帶寬,也能降低服務(wù)器的負(fù)載。
在nginx中配置gzip比較簡單
一般情況下只要在nginx.conf的http段中加入下面幾行配置即可
?gzip?on; ?gzip_min_length?1000; ?gzip_buffers??48k; ?gzip_types??text/plain?application/x-javascript?text/css?text/html?application/xml;
可以通過網(wǎng)頁gzip檢測工具來檢測網(wǎng)頁是否啟用了gzip
臨時重定向示例:訪問www.lansgg.com/c 重定向到www.lansgg.com/cc
編輯nginx.conf
?server?{ ??listen?80?default_server; ??server_name??www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ??access_log??logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ??error_log??logs/lansgg.error.log; ??root???/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ??index?index.html; ??rewrite?^/c/(.*)$?http://www.lansgg.com/cc/$1; ??} ??? [root@master?lansgg]#?tree . ├──?c │?└──?index.html ├──?cc │?└──?index.html ├──?index.html └──?it.jpg ? 2?directories,?4?files
訪問http://www.lansgg.com/c 會跳轉(zhuǎn)到http://www.lansgg.com/cc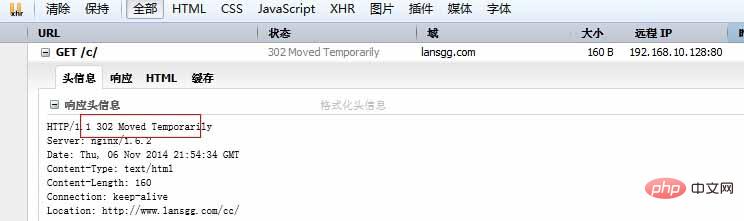
302即為臨時重定向;
永久重定向(隱含重定向)
編輯nginx.conf
?server?{ ??listen?80?default_server; ??server_name??www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ??access_log??logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ??error_log??logs/lansgg.error.log; ??root???/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ??index?index.html; ??rewrite?^/c/(.*)$?/cc/$1; ??}
訪問 http://www.lansgg.com/c/ 頁面顯示的是跳轉(zhuǎn)后的頁面,可是url卻沒有變化;firebug也看不到302代碼信息;現(xiàn)在它其實是301;
2、反向代理:是指以代理服務(wù)器來接受internet上的連接請求,然后將請求轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)給內(nèi)部網(wǎng)絡(luò)上的服務(wù)器,并將從服務(wù)器上得到的結(jié)果返回給internet上請求連接的客戶端,此時代理服務(wù)器對外就表現(xiàn)為一個服務(wù)器。
2.1、配置nginx實現(xiàn)反向代理;
需求:訪問http://192.168.10.128/other 返回 apache主機(jī)的other目錄下的index.html
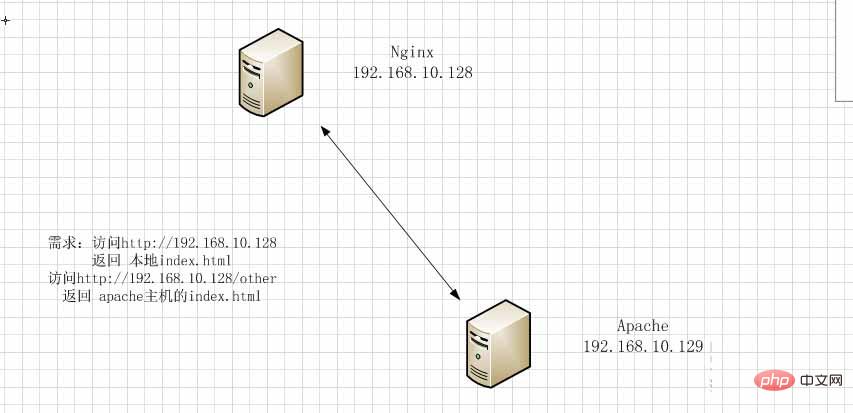
涉及nginx指令:
語法:proxy_pass url???
可使用字段:location, location中的if字段??????
這個指令設(shè)置被代理服務(wù)器的地址和被映射的uri,地址可以使用主機(jī)名或ip加端口號的形式,例如:proxy_pass http://192.168.10.129/url
2.2、配置nginx配置文件nginx.conf
?server?{ ?listen?80?default_server; ?server_name?www.lansgg.com?lansgg.com; ?access_log?logs/lansgg.access.log?main; ?error_log?logs/lansgg.error.log; ?root??/opt/nginx/nginx/html/lansgg; ?location?/?{ ??index?index.html; ??} ?location?/other?{ ?proxy_pass???http://192.168.10.129/other; ?proxy_set_header?x-real-ip?$remote_addr;? ??} ?}
2.3、配置client1
mkdir?/var/www/html/other echo?"192.168.10.129"?>?/var/www/html/other/index.html
2.4、測試;
訪問url:??? http://www.lansgg.com/other???? 你會發(fā)現(xiàn)跳轉(zhuǎn)到了 : http://192.168.10.129/other/
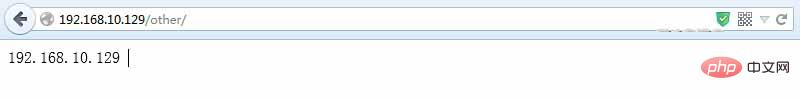
查看日志:
[root@client1?~]#?tail?-f?/var/log/httpd/access_log? 192.168.10.1?-?-?[06/nov/2014:21:25:44?+0800]?"get?/other/?http/1.1"?200?15?"-"?"mozilla/5.0?(windows?nt?6.1;?wow64;?rv:32.0)?gecko/20100101?firefox/32.0"
.jpg)















.png)
