單表查詢指的是在一張表中進行數據的查詢,它的執行順序是“from->where->group by->having->distinct->order by->limit->select”。

在數據庫操作中,單表查詢就是在一張表中進行數據的查詢,詳細它的語法是:
select?distinct?字段1,字段2...?from?表名 where?分組之前的過濾條件 group?by?分組字段 having?分組之后的過濾條件 order?by?排序字段 limit?顯示的條數;
語法是樣的一個順序,但是它的執行順序就不是從語法的順序來執行了,而是這樣的一個順序。
? ? from—>where—>group by—>having–>distinct—>order by—>limit—>select
至于為什么這樣的一個執行順序,我就不說了,也沒這個自信說清楚。如果小白只要記得是這個執行順序就可以了,如果非要刨根問底,可以去google一下。
在了解單表查詢前,我們首先來建一張雇員表:
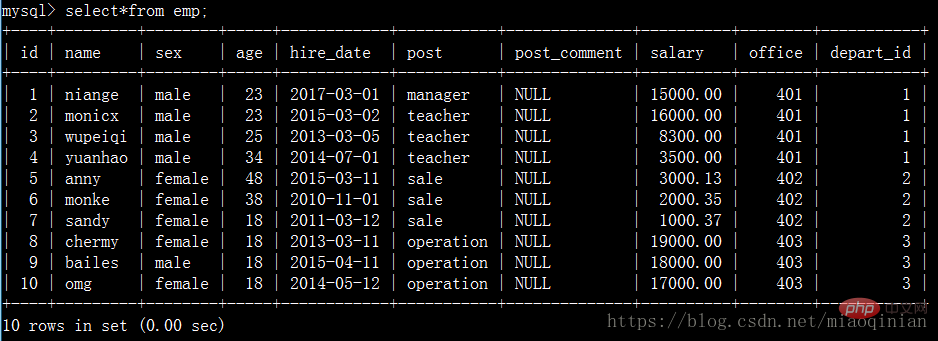
emp表: 員工id??????id??????????????????int????????????? 姓名????????emp_name????????????varchar 性別????????sex?????????????????enum 年齡????????age?????????????????int 入職日期????hire_date???????????date 崗位????????post????????????????varchar 職位描述????post_comment????????varchar 薪水????????salary??????????????double 辦公室??????office??????????????int 部門編號????depart_id???????????int
建表:
create?table?emp( id?int?not?null?unique?auto_increment, name?varchar(20)?not?null, sex?enum('male','female')?not?null?default?'male',? age?int(3)?unsigned?not?null?default?28, hire_date?date?not?null, post?varchar(50), post_comment?varchar(100), salary?double(15,2), office?int,? depart_id?int );
插入數據:
insert?into?emp(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id)?values ('niange','male',23,'20170301','manager',15000,401,1),? ('monicx','male',23,'20150302','teacher',16000,401,1), ('wupeiqi','male',25,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1), ('yuanhao','male',34,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1), ('anny','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2), ('monke','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2), ('sandy','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2), ('chermy','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3), ('bailes','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3), ('omg','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3);
where條件過濾
where字句中可以使用:
1. 比較運算符:>、=、 、!=。
2. between 1 and 5 值在1到5之間。
3. in(1,3,8) 值是1或3或8。
4. like ‘monicx%’
? ? %表示任意多字符
? ? _表示一個字符?
5. 邏輯運算符:在多個條件直接可以使用邏輯運算符 and、or、not。
6、正則表達式
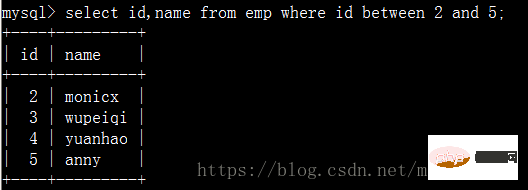
查找員工id在2到5之間的名字:
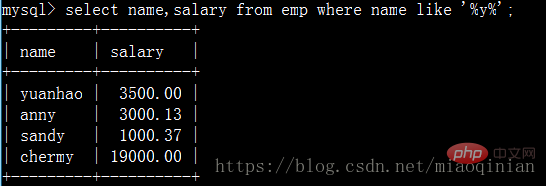
?查詢員工姓名中包含y字母的員工姓名與其薪資:
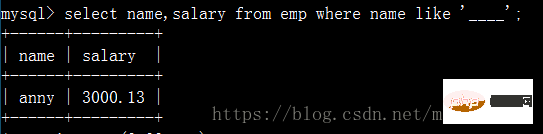
查詢員工姓名是由四個字符組成的的員工姓名與其薪資:
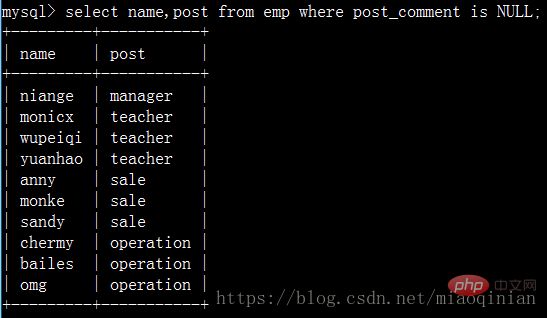
查詢崗位描述為空的員工名與崗位名:
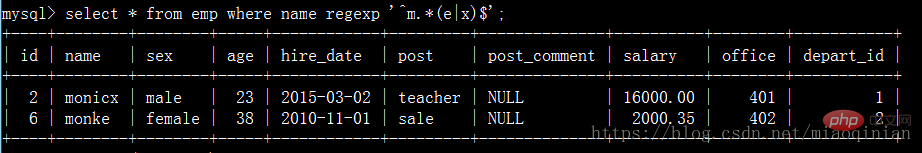
查詢名字是字母m開頭,以字母e或x結尾的員工!些時就可以用到正則表達示了,mysql里提供了regexp來現正則。
group by分組
先設置mysq的sql_mode為only_full_group_by,意味著以后但凡分組,只能取到分組的依據。
set?global?sql_mode="strict_trans_tables,only_full_group_by";
分組發生在where之后,即分組是基于where之后得到的記錄而進行的。
分組指的是:將所有記錄按照某個相同字段進行歸類,比如針對員工信息表的職位分組,或者按照性別進行分組等
怎么要分組呢?
? ? 如:取每個部門的最高工資。
? ? 如:取每個部門的員工數。
每’這個字后面的字段,就是我們分組的依據。
注意:我們可以按照任意字段分組,但是分組完畢后,比如group by post,只能查看post字段。
但如果想查看組內信息,需要借助于聚合(聚在一起合成一個內容)函數
每個部門的最高工資 select?post,max(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; 每個部門的最底工資 select?post,min(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; 每個部門的平均工資 select?post,avg(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; 每個部門的工資總合 select?post,sum(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; 每個部門的總人數 select?post,count(id)?from?emp?group?by?post;
group_concat(分組之后用來用它獲得組內字段的內容。)
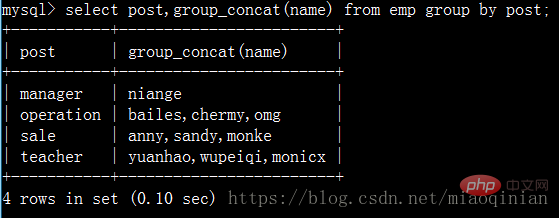
而且它還可以這樣子使用:
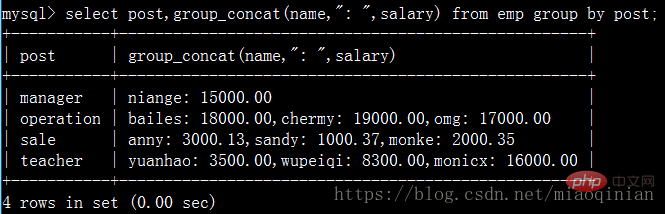
可以用下面的代碼自己試一下吧:
select?post,group_concat(name)?from?emp?group?by?post; select?post,group_concat(name,"_NB")?from?emp?group?by?post; select?post,group_concat(name,":?",salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; select?post,group_concat(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post;
機智的同學會說那么不分組的情況下也能用它嗎?不行!但是mysql提拱了另外的方式來操作。它就是concat。
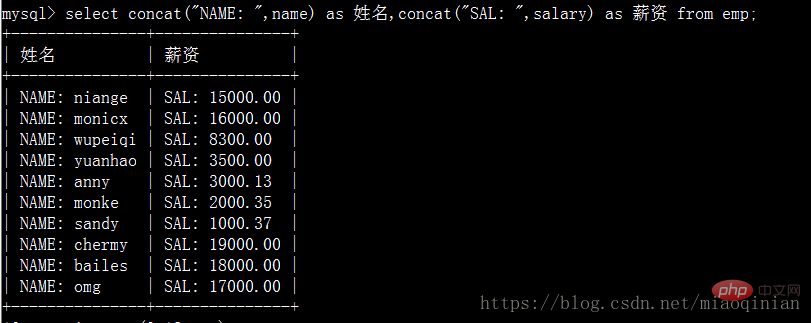
# 補充as語法 mysql> select emp.id,emp.name from emp as t1; # 報錯 mysql> select t1.id,t1.name from emp as t1;
group by 就說這些了,如果還不懂,可以作一下面的小練習。
????1.?查詢崗位名以及崗位包含的所有員工名字 ????????select?post,group_concat(name)?from?emp?group?by?post; ????2.?查詢崗位名以及各崗位內包含的員工個數 ????????select?post,count(id)?from?emp?group?by?post; ????3.?查詢公司內男員工和女員工的個數 ????????select?sex,count(id)?from?emp?group?by?sex; ????4.?查詢崗位名以及各崗位的平均薪資 ????????select?post,avg(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; ????5.?查詢崗位名以及各崗位的最高薪資 ????????select?post,max(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; ????6.?查詢崗位名以及各崗位的最低薪資 select?post,min(salary)?from?emp?group?by?post; ????7.?查詢男員工與男員工的平均薪資,女員工與女員工的平均薪資 ????????select?sex,avg(salary)?from?emp?group?by?sex; ????8、統計各部門年齡在30歲以上的員工平均工資 ???????select?post,avg(salary)?from?emp?where?age?>=?30?group?by?post;
having過濾
having的語法格式與where一模一樣,只不過having是在分組之后進行的進一步過濾。
where不能用聚合函數,但having是可以用聚合函數,這也是它們最大的區別。
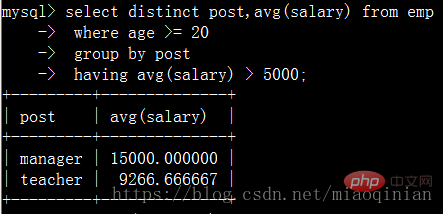
統計各部門年齡在24歲以上的員工平均工資,并且保留平均工資大于4000的部門。
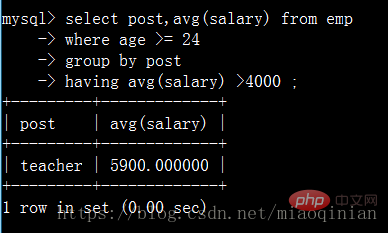
注意:having只能與 select 語句一起使用。
having通常在 group by 子句中使用。
如果不使用 group by子句,不會報錯,但會出現以下的情況。
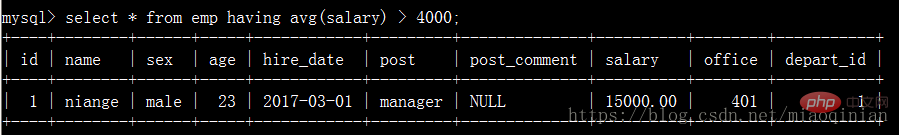
distinct去重
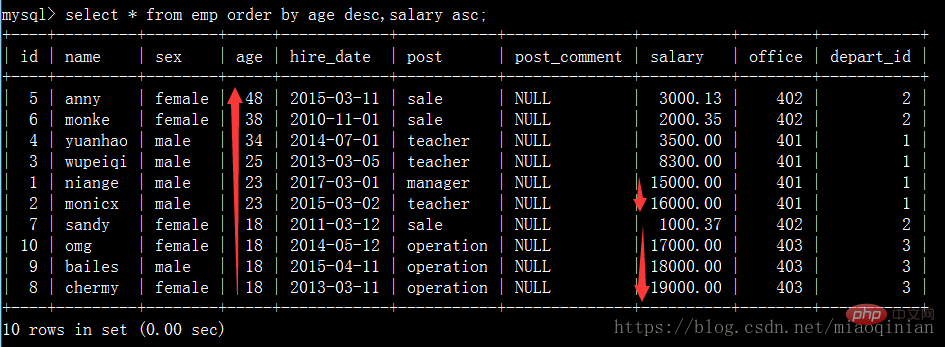
order by 排序
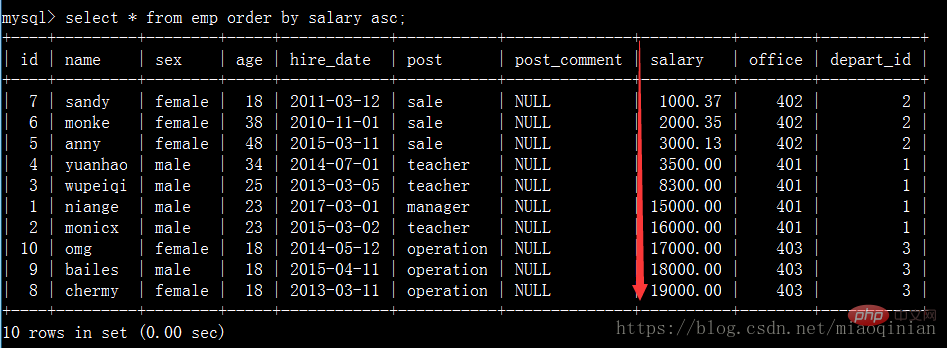
select * from emp order by salary asc; #默認升序排 select * from emp order by salary desc; #降序排 select * from emp order by age desc; #降序排 select * from emp order by age desc,salary asc; #先按照age降序排,再按照薪資升序排
limit 限制顯示條數
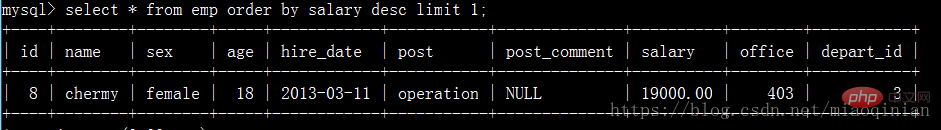
如查要獲取工資最高的員工的信息,我們可以用order by和limit也可以做到。
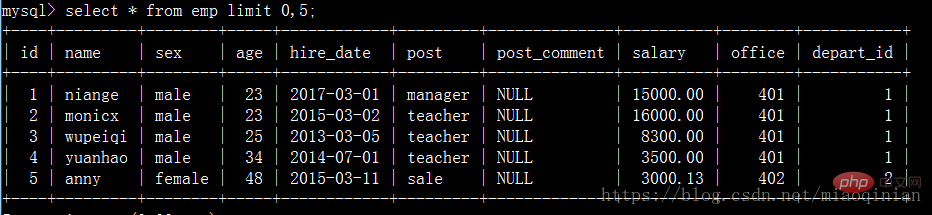
如果查一個表數據量大的話可以用limit分頁顯示。
select * from emp limit 0,5;
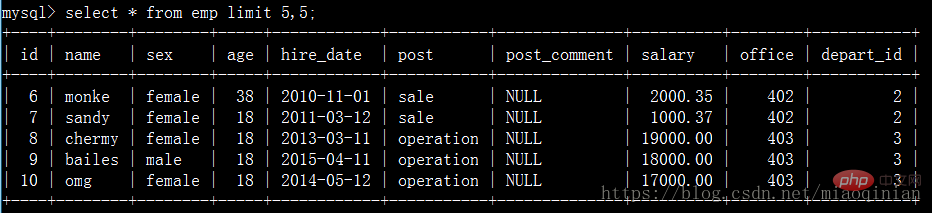
select * from emp limit 5,5;
ps:看到這里如果上面的東西你都明白的話,單表查詢你基本上已經熟悉它了。