區(qū)別:1、db2用“create table a like b”創(chuàng)建類似表,oracle用“create table a as select * from b”;2、db2用varchar類型轉(zhuǎn)換,oracle用“to_char”函數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換。

本教程操作環(huán)境:Windows10系統(tǒng)、Oracle 11g版、Dell G3電腦。
db2與oracle的sql語句有什么區(qū)別
1.創(chuàng)建類似表語法
Oracle : create table a as select * from b; DB2 : create table a like b; (8版本有效,9版本無效) create table new_a as select col1,col2... from a definition only
2.快速清空大表語法
Oracle : truncate table a; DB2 : alter table a active not logged initially with empty table;
3.取前N條數(shù)據(jù)語法
Oracle : select * from a where rownum <= N; DB2 : select * from a fetch first N rows only;
4.取得系統(tǒng)時間語法
Oracle : select sysdate from dual; DB2 : select current timestamp from sysibm.sysdummy1;
5.空值轉(zhuǎn)換方式不同
Oracle : select col1,col2,nvl(col3,'0') from tablename; (判斷col3字段是否為空,不為空就輸出原來的數(shù)值,為空就輸出0) DB2 : select col1,col2,value(col3,'0') from tablename; (mysql和Db2可以使用Coalesce(col3,'0')函數(shù)來實現(xiàn)上述功能)
Coalesce()函數(shù)
這個函數(shù)主要用來進(jìn)行空值處理,其參數(shù)格式如下: COALESCE ( expression,value1,value2……,valuen) COALESCE()函數(shù)的第一個參數(shù)expression為待檢測的表達(dá)式,而其后的參數(shù)個數(shù)不定。 COALESCE()函數(shù)將會返回包括expression在內(nèi)的所有參數(shù)中的第一個非空表達(dá)式。 如果expression不為空值則返回expression; 否則判斷value1是否是空值,如果value1不為空值則返回value1; 否則判斷value2是否是空值,如果value2不為空值則返回value2; ……以此類推, 如果所有的表達(dá)式都為空值,則返回NULL。
6.類型轉(zhuǎn)換方式不同
oracle : select to_char(sysdate,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') from dual; DB2 : select varchar(current timestamp) from sysibm.sysdummy1;
解析:
Oracle數(shù)據(jù)類型改變函數(shù):to_char()、to_date()、to_number()等; 如果僅僅取年,月,日等,可以用 to_char(sysdate, 'YYYY'), to_char('MM') , to_char('DD')取得。 只取年月日TRUNC(SYSDATE)。 取時分秒TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'HH24:MI:SS')。 DB2數(shù)據(jù)類型改變函數(shù):char()、varchar()、int()、date()、time()等; 取得年,月,日等的寫法: YEAR(current timestamp), MONTH(current timestamp), DAY(current timestamp), HOUR(current timestamp), MINUTE(current timestamp), SECOND(current timestamp), MICROSECOND(current timestamp), 只取年月日可以用 DATE(current timestamp), 取時分秒 TIME(current timestamp)。 Char()是定長字符串(1-255),varchar()為非定長字符串(1-32672)日期, 時間形態(tài)變?yōu)樽址螒B(tài): char(current date), char(current time) 將字符串轉(zhuǎn)換成日期或時間形態(tài): TIMESTAMP('2002-10-2012:00:00'), DATE('2002-10-20'), DATE('10/20/2002'), TIME('12:00:00')
目前DB2 V8也支持to_char和to_date,V9版新增了to_number
7.字符串轉(zhuǎn)換為日期方式不同(To_Number/cast)
Oracle: select to_number('123') from dual; select cast('123' as integer) from dual; DB2 : select cast('123' as integer) from sysibm.sysdummy1; select cast(current time as char(8)) from sysibm.sysdummy1;
8.子查詢
Oracle: 直接用子查詢 Db2:WITH語句 WITH a1 AS(SELECT max(id) AS aa1 FROM test )SELECT id ,aa1 FROM test ,a1
9.遞歸查詢(分層查詢)
Oracle遞歸查詢:CONNECT BY PRIOR ... START WITH ... DB2 遞歸查詢:DB2較難理解,要WITH一個虛擬表
Oracle:
//從child是son的數(shù)據(jù)向上查詢出所有的長輩select distinct test_parent from ( select t.test_parent from t_test t connect by prior t.test_parent = t.test_child start with t.test_child = 'son' )
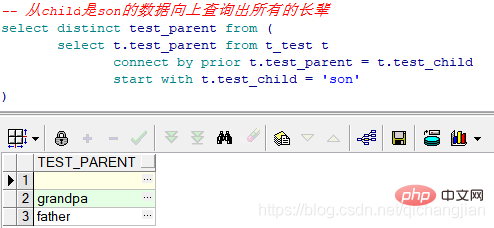
了解更多:Oracle分層查詢(遞歸查詢):start with…connect by prior 以及 level關(guān)鍵字
DB2:
// Db2遞歸查詢寫法with par_test(test_child,test_parent) as( select test_child,test_parent from t_test where child='grandchild' -- 設(shè)置遞歸起點 union all select t.test_child,t.test_parent from par_test pt,t_test t where pt.test_parent = t.test_child ----遞歸的方向為從子向父)select distinct test_parent from par_test


如上圖,從grandchild開始查詢其所有的父節(jié)點,首先設(shè)定虛擬表起點,即左邊第四行;依次往上推,其父親是son = 上一行的child,即VT.parent = T.child…
最后查詢結(jié)果為:
| test_parent |
|---|
| son |
| father |
| grandpa |
10.數(shù)據(jù)類型有差別
比較大的差別: 1. char大小對比 Oracle: char 2000 DB2 : char 254 2. 日期類型 Oracle: date datetime DB2 :date(日期) time(時間)timestamp(日期時間)
11.關(guān)于rowId
Oracle中它是由數(shù)據(jù)庫唯一產(chǎn)生的,在程序中可以獲得 DB2 在V8版本才有此功能
12.decode方法
Oracle: decode方法(decode(條件,值1,翻譯值1,值2,翻譯值2,...,值n,翻譯值n,缺省值)) 【函數(shù)用法在下邊有鏈接】 或者 case語句 DB2: 只有case表達(dá)式 示例語句: select id,name, case when integer(flag)=0 then '假' when integer(flag)=1 then '真' else '異常' end from test 或者 select id,name, case integer(flag) when 0 then '假' when 1 then '真' else '異常' end from test
推薦教程:《Oracle視頻教程》
? 版權(quán)聲明
文章版權(quán)歸作者所有,未經(jīng)允許請勿轉(zhuǎn)載。
THE END
喜歡就支持一下吧
相關(guān)推薦
















.png)
