下面由laravel框架教程欄目給大家介紹Laravel運行原理,希望對需要的朋友有所幫助!
前言
知其然知其所以然,剛開始接觸框架的時候大不部分人肯定一臉懵逼,不知道如何實現(xiàn)的,沒有一定的基礎(chǔ)知識,直接去看框架的源碼,只會被直接勸退,laravel 框架是一款非常優(yōu)秀的 php 框架,這篇文章就是帶你徹底搞懂框架的運行原理,好讓你在面試的過程中有些談資(吹牛),學(xué)習(xí)和研究優(yōu)秀框架的源碼也有助于我們自身技術(shù)的提升,接下來系好安全帶,老司機(jī)要開始開車了!!!
準(zhǔn)備知識
- 熟悉 php 基本知識,如常見的數(shù)組方法,閉包函數(shù)的使用,魔術(shù)方法的使用
- 熟悉 php 的反射機(jī)制和依賴注入
- 熟悉 php 命名空間概念和 compose 自動加載
- 熟悉常見的設(shè)計模式,包括但是不限于單例模式,工廠模式,門面模式,注冊樹模式,裝飾者模式等
運行原理概述
Laravel 框架的入口文件 index.php
1、引入自動加載 autoload.php 文件
2、創(chuàng)建應(yīng)用實例,并同時完成了
基本綁定($this、容器類Container等等)、 基本服務(wù)提供者的注冊(Event、log、routing)、 核心類別名的注冊(比如db、auth、config、router等)
3、開始 http 請求的處理
make?方法從容器中解析指定的值為實際的類,比如?$app->make(IlluminateContractsHttpKernel::class);?解析出來?AppHttpKernel? handle?方法對?http?請求進(jìn)行處理 實際上是?handle?中?sendRequestThroughRouter?處理?http?的請求 首先,將?request?綁定到共享實例 然后執(zhí)行?bootstarp?方法,運行給定的引導(dǎo)類數(shù)組?$bootstrappers,這里是重點,包括了加載配置文件、環(huán)境變量、服務(wù)提供者、門面、異常處理、引導(dǎo)提供者等 之后,進(jìn)入管道模式,經(jīng)過中間件的處理過濾后,再進(jìn)行用戶請求的分發(fā) 在請求分發(fā)時,首先,查找與給定請求匹配的路由,然后執(zhí)行?runRoute?方法,實際處理請求的時候?runRoute?中的?runRouteWithinStack? 最后,經(jīng)過?runRouteWithinStack?中的?run?方法,將請求分配到實際的控制器中,執(zhí)行閉包或者方法,并得到響應(yīng)結(jié)果
4、 將處理結(jié)果返回
詳細(xì)源碼分析
1、注冊自動加載類,實現(xiàn)文件的自動加載
require __DIR__.'/../vendor/autoload.php';
2、創(chuàng)建應(yīng)用容器實例 Application (該實例繼承自容器類 Container),并綁定核心(web、命令行、異常),方便在需要的時候解析它們
$app = require_once __DIR__.'/../bootstrap/app.php';
app.php 文件如下:
<?php // 創(chuàng)建Laravel實例 【3】 $app = new IlluminateFoundationApplication( $_ENV['APP_BASE_PATH'] ?? dirname(__DIR__) ); // 綁定Web端kernel $app->singleton( ?IlluminateContractsHttpKernel::class,?AppHttpKernel::class); //?綁定命令行kernel $app->singleton( ?IlluminateContractsConsoleKernel::class,?AppConsoleKernel::class); //?綁定異常處理 $app->singleton( ?IlluminateContractsDebugExceptionHandler::class,?AppExceptionsHandler::class); //?返回應(yīng)用實例 return?$app;
3、在創(chuàng)建應(yīng)用實例(Application.php)的構(gòu)造函數(shù)中,將基本綁定注冊到容器中,并注冊了所有的基本服務(wù)提供者,以及在容器中注冊核心類別名
3.1、將基本綁定注冊到容器中
????/** ?????*?Register?the?basic?bindings?into?the?container. ?????* ?????*?@return?void ?????*/ ????protected?function?registerBaseBindings() ????{ ????????static::setInstance($this); ????????$this->instance('app',?$this); ????????$this->instance(Container::class,?$this); ????????$this->singleton(Mix::class); ????????$this->instance(PackageManifest::class,?new?PackageManifest( ????????????new?Filesystem,?$this->basePath(),?$this->getCachedPackagesPath() ????????)); ????????#?注:instance方法為將...注冊為共享實例,singleton方法為將...注冊為共享綁定 ????}
3.2、注冊所有基本服務(wù)提供者(事件,日志,路由)
protected?function?registerBaseServiceProviders() ????{ ????????$this->register(new?EventServiceProvider($this)); ????????$this->register(new?LogServiceProvider($this)); ????????$this->register(new?RoutingServiceProvider($this)); ????}
3.3、在容器中注冊核心類別名
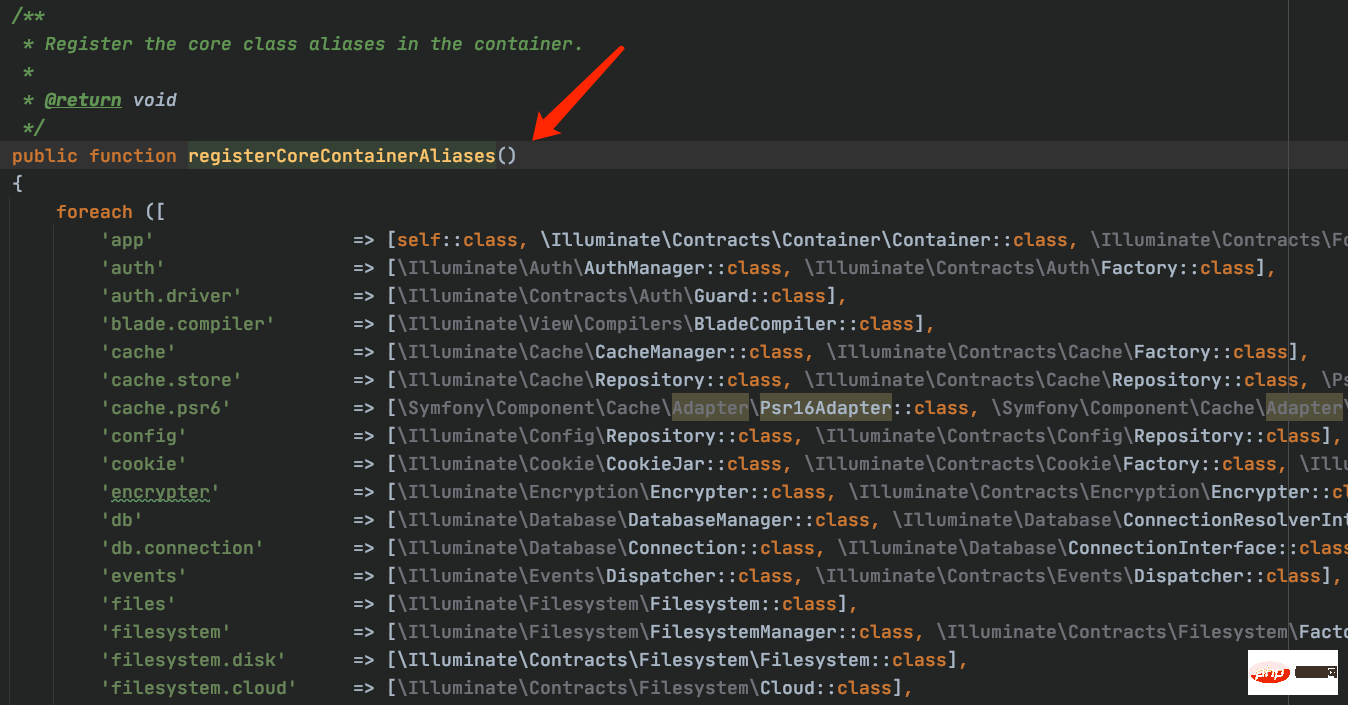
4、上面完成了類的自動加載、服務(wù)提供者注冊、核心類的綁定、以及基本注冊的綁定
5、開始解析 http 的請求
index.php //5.1 $kernel?=?$app->make(IlluminateContractsHttpKernel::class); //5.2 $response?=?$kernel->handle( ?$request?=?IlluminateHttpRequest::capture());
5.1、make方法是從容器解析給定值
$kernel?=?$app->make(IlluminateContractsHttpKernel::class); 中的IlluminateContractsHttpKernel::class?是在index.php?中的$app?=?require_once?__DIR__.'/../bootstrap/app.php';這里面進(jìn)行綁定的,實際指向的就是AppHttpKernel::class這個類
5.2、這里對 http 請求進(jìn)行處理
$response = $kernel->handle( $request = IlluminateHttpRequest::capture());
進(jìn)入 $kernel 所代表的類 AppHttpKernel.php 中,我們可以看到其實里面只是定義了一些中間件相關(guān)的內(nèi)容,并沒有 handle 方法
我們再到它的父類 use IlluminateFoundationHttpKernel as HttpKernel; 中找 handle 方法,可以看到 handle 方法是這樣的
public function handle($request){ try { $request->enableHttpMethodParameterOverride(); // 最核心的處理http請求的地方【6】 $response = $this->sendRequestThroughRouter($request); } catch (Exception $e) { $this->reportException($e); $response = $this->renderException($request, $e); } catch (Throwable $e) { $this->reportException($e = new FatalThrowableError($e)); $response = $this->renderException($request, $e); } $this->app['events']->dispatch( new EventsRequestHandled($request, $response) ); return $response;}
6、處理 Http 請求(將 request 綁定到共享實例,并使用管道模式處理用戶請求)
vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Http/Kernel.php的handle方法// 最核心的處理http請求的地方$response = $this->sendRequestThroughRouter($request);protected function sendRequestThroughRouter($request){ // 將請求$request綁定到共享實例 $this->app->instance('request', $request); // 將請求request從已解析的門面實例中清除(因為已經(jīng)綁定到共享實例中了,沒必要再浪費資源了) Facade::clearResolvedInstance('request'); // 引導(dǎo)應(yīng)用程序進(jìn)行HTTP請求 $this->bootstrap();【7、8】 // 進(jìn)入管道模式,經(jīng)過中間件,然后處理用戶的請求【9、10】 return (new Pipeline($this->app)) ->send($request) ->through($this->app->shouldSkipMiddleware() ? [] : $this->middleware) ->then($this->dispatchToRouter());}
7、在 bootstrap 方法中,運行給定的 引導(dǎo)類數(shù)組 $bootstrappers,加載配置文件、環(huán)境變量、服務(wù)提供者、門面、異常處理、引導(dǎo)提供者,非常重要的一步,位置在 vendor/laravel/framework/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Http/Kernel.php
/** * Bootstrap the application for HTTP requests. * * @return void */public function bootstrap(){ if (! $this->app->hasBeenBootstrapped()) { $this->app->bootstrapWith($this->bootstrappers()); }}
/** * 運行給定的引導(dǎo)類數(shù)組 * * @param string[] $bootstrappers * @return void */public function bootstrapWith(array $bootstrappers){ $this->hasBeenBootstrapped = true; foreach ($bootstrappers as $bootstrapper) { $this['events']->dispatch('bootstrapping: '.$bootstrapper, [$this]); $this->make($bootstrapper)->bootstrap($this); $this['events']->dispatch('bootstrapped: '.$bootstrapper, [$this]); }}/** * Get the bootstrap classes for the application. * * @return array */protected function bootstrappers(){ return $this->bootstrappers;}/** * 應(yīng)用程序的引導(dǎo)類 * * @var array */protected $bootstrappers = [ // 加載環(huán)境變量 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapLoadEnvironmentVariables::class, // 加載config配置文件【重點】 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapLoadConfiguration::class, // 加載異常處理 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapHandleExceptions::class, // 加載門面注冊 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapRegisterFacades::class, // 加載在config/app.php中的providers數(shù)組里所定義的服務(wù)【8 重點】 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapRegisterProviders::class, // 記載引導(dǎo)提供者 IlluminateFoundationBootstrapBootProviders::class,];
8、加載 config/app.php 中的 providers 數(shù)組里定義的服務(wù)
IlluminateAuthAuthServiceProvider::class,IlluminateBroadcastingBroadcastServiceProvider::class,....../** * 自己添加的服務(wù)提供者 */AppProvidersHelperServiceProvider::class,
可以看到,關(guān)于常用的 redis、Session、queue、auth、database、Route 等服務(wù)都是在這里進(jìn)行加載的
9、使用管道模式處理用戶請求,先經(jīng)過中間件進(jìn)行處理和過濾
return (new Pipeline($this->app)) ->send($request) // 如果沒有為程序禁用中間件,則加載中間件(位置在app/Http/Kernel.php的$middleware屬性) ->through($this->app->shouldSkipMiddleware() ? [] : $this->middleware) ->then($this->dispatchToRouter());}
app/Http/Kernel.php
/** * 應(yīng)用程序的全局HTTP中間件 * * These middleware are run during every request to your application. * * @var array */protected $middleware = [ AppHttpMiddlewareTrustProxies::class, AppHttpMiddlewareCheckForMaintenanceMode::class, IlluminateFoundationHttpMiddlewareValidatePostSize::class, AppHttpMiddlewareTrimStrings::class, IlluminateFoundationHttpMiddlewareConvertEmptyStringsToNull::class,];
10、經(jīng)過中間件處理后,再進(jìn)行請求分發(fā)(包括查找匹配路由)
/** * 10.1 通過中間件/路由器發(fā)送給定的請求 * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return IlluminateHttpResponse */ protected function sendRequestThroughRouter($request){ ... return (new Pipeline($this->app)) ... // 進(jìn)行請求分發(fā) ->then($this->dispatchToRouter());}
/** * 10.2 獲取路由調(diào)度程序回調(diào) * * @return Closure */protected function dispatchToRouter(){ return function ($request) { $this->app->instance('request', $request); // 將請求發(fā)送到應(yīng)用程序 return $this->router->dispatch($request); };}
/** * 10.3 將請求發(fā)送到應(yīng)用程序 * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return IlluminateHttpResponse|IlluminateHttpJsonResponse */ public function dispatch(Request $request){ $this->currentRequest = $request; return $this->dispatchToRoute($request);}
/** * 10.4 將請求分派到路由并返回響應(yīng)【重點在runRoute方法】 * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return IlluminateHttpResponse|IlluminateHttpJsonResponse */public function dispatchToRoute(Request $request){ return $this->runRoute($request, $this->findRoute($request));}
/** * 10.5 查找與給定請求匹配的路由 * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return IlluminateRoutingRoute */protected function findRoute($request){ $this->current = $route = $this->routes->match($request); $this->container->instance(Route::class, $route); return $route;}
/** * 10.6 查找與給定請求匹配的第一條路由 * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return IlluminateRoutingRoute * * @throws SymfonyComponentHttpKernelExceptionNotFoundHttpException */public function match(Request $request){ // 獲取用戶的請求類型(get、post、delete、put),然后根據(jù)請求類型選擇對應(yīng)的路由 $routes = $this->get($request->getMethod()); // 匹配路由 $route = $this->matchAgainstRoutes($routes, $request); if (! is_null($route)) { return $route->bind($request); } $others = $this->checkForAlternateVerbs($request); if (count($others) > 0) { return $this->getRouteForMethods($request, $others); } throw new NotFoundHttpException;}
到現(xiàn)在,已經(jīng)找到與請求相匹配的路由了,之后將運行了,也就是 10.4 中的 runRoute 方法
/** * 10.7 返回給定路線的響應(yīng) * * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @param IlluminateRoutingRoute $route * @return IlluminateHttpResponse|IlluminateHttpJsonResponse */protected function runRoute(Request $request, Route $route){ $request->setRouteResolver(function () use ($route) { return $route; }); $this->events->dispatch(new EventsRouteMatched($route, $request)); return $this->prepareResponse($request, $this->runRouteWithinStack($route, $request) );}
/** * Run the given route within a Stack "onion" instance. * 10.8 在棧中運行路由,先檢查有沒有控制器中間件,如果有先運行控制器中間件 * * @param IlluminateRoutingRoute $route * @param IlluminateHttpRequest $request * @return mixed */protected function runRouteWithinStack(Route $route, Request $request){ $shouldSkipMiddleware = $this->container->bound('middleware.disable') && $this->container->make('middleware.disable') === true; $middleware = $shouldSkipMiddleware ? [] : $this->gatherRouteMiddleware($route); return (new Pipeline($this->container)) ->send($request) ->through($middleware) ->then(function ($request) use ($route) { return $this->prepareResponse( $request, $route->run() ); });}
/** * Run the route action and return the response. * 10.9 最后一步,運行控制器的方法,處理數(shù)據(jù) * @return mixed */ public function run() { $this->container = $this->container ?: new Container; try { if ($this->isControllerAction()) { return $this->runController(); } return $this->runCallable(); } catch (HttpResponseException $e) { return $e->getResponse(); } }
11、運行路由并返回響應(yīng)(重點)
可以看到,10.7 中有一個方法是 prepareResponse,該方法是從給定值創(chuàng)建響應(yīng)實例,而 runRouteWithinStack 方法則是在棧中運行路由,也就是說,http 的請求和響應(yīng)都將在這里完成。
總結(jié)
到此為止,整個 Laravel 框架的運行流程就分析完畢了,揭開了 Laravel 框架的神秘面紗,其中為了文章的可讀性,只給出了核心代碼,需要大家結(jié)合文章自行去閱讀源碼,需要注意的是必須了解文章中提到的準(zhǔn)備知識,這是閱讀框架源碼的前提和基礎(chǔ),希望大家有所收獲,下車!!!? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?


















.png)

